
Bodi Construction Vehicles
Car parts are divided into two major groups, namely the body and chassis. Bodi is part of a vehicle that is formed in such a way, (in general) made of metal plate material (steel plate) the thickness between 0.6 mm - 0.9 mm as a place of passengers or goods.
Is part of the vehicle chassis which serves as the support body and consists of the frame (frame), engine (engine), power train (power transfer), wheels (the wheels), steering system (steering system), suspension system (suspension system) , brake system (brake system) and other equipment.
Based on the attachment of the body on frame construction, there are two types of vehicle body construction, ie composite construction (separate) and construction monocoq (fused). Frame is attached to his place all the components of the vehicle including the body. Order to be strong, lightweight, sturdy and resistant to vibration, or shock received from the condition of the road. To be strong then there is a box truss construction, pipe or U shape, which generally consists of two pieces of elongated and connected by a cross-section. At the beginning of technology development vehicle body and frame, body and frame are made separately (composite body) but lately the body and frame are made together (monocoque body, also called the integral body), especially in sedan cars.
Construction Analysis (Composite)
Is a type vehicle body construction in which a separate body and chassis. Linkage / connections between body and frame using bolts and nuts. To improve comfort during use, then the frame is installed between the body and as a means of rubber vibration dampers.
Construction framework of a separate body and this provides ease in replacing vehicle body parts were damaged, especially the lower body or the breakup order. This construction is usually used in old type sedan vehicles, passenger vehicles and freight cars. (Eg trucks, buses, pick-ups, etc.).
Because the body and frame together, then the shape can be lower than with the composite type so that the center of gravity lower gravity will cause the vehicle more stable. This construction was used on the sedan, even a few vehicles MPV (Multi Purpose Vehicle) began implementing monocoq body construction.
Frame Types
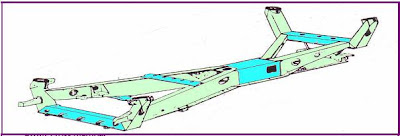
Based on the shape, the vehicle frame is divided into several types, namely: (a) to form H, (b) order the perimeter, (c) to form X, (d) to form the spine (backbone), and the order form the floor (platform frame ).
Order form H.
Construction is very simple, easy to manufacture, are widely used for buses, trucks.
Perimeter frame.
Perimeter frame is an improved form of H, the body attached to the edge of the frame so the floor can be lowered position. The decrease will lower the vehicle floor the focal point of heavy vehicles and vehicle height is reduced so that the driving steady, passenger space becomes more flexible, widely used for the sedan.
Order form X.
Beam frame construction consisting of two rod-shaped main frame longitudinal beams together in the middle. Place of linkage with body and doors can be made low, so easy in and out of vehicles, robust against rotation, used to the old type sedans.
Order forms Spine (Back Bone).
Construction framework of a single model framework, the burden of the middle (back) and arms that stand out as the holder body. This kind of frame construction also allows the central point made lower vehicle weight. Frame construction this model is often used for passenger cars and trucks.
Floor Model framework (Platform Frame).
Body and frame is welded into one, so it is a form that is integrated, allowing the interior space is made large. Another advantage the use of frame construction this model is to have a fairly good resistance against bending and torsion.
BODY AUTOMOTIVE Vol 1





Comments
Post a Comment